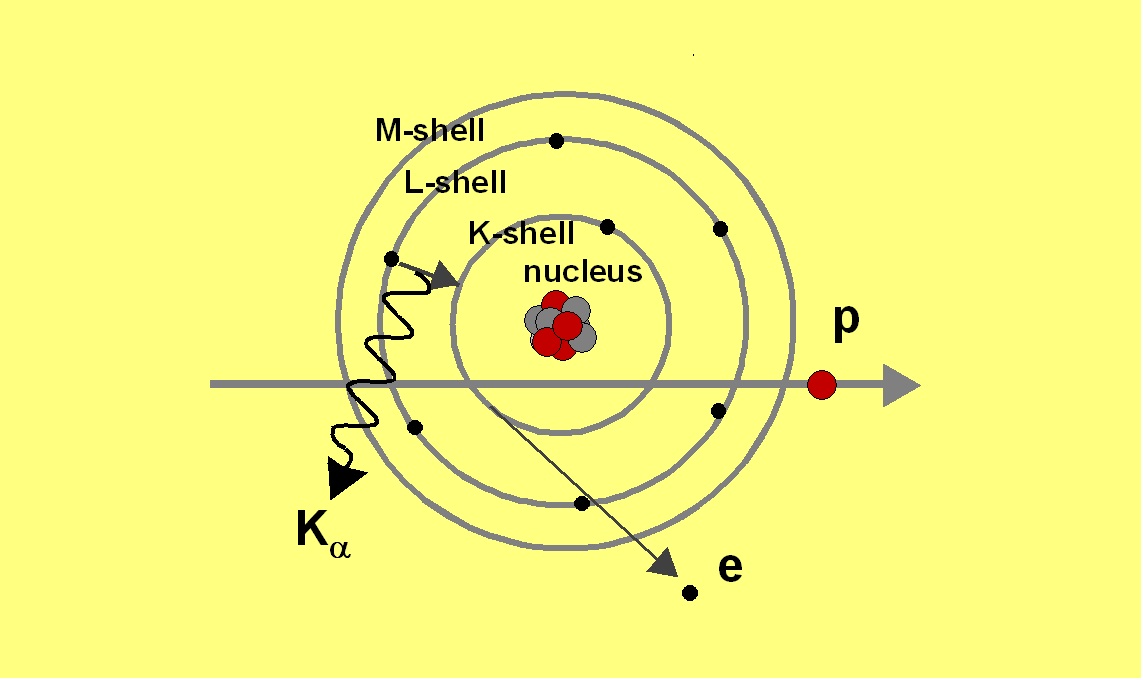
 Fig. Principle of particle-induced X-ray emission
Fig. Principle of particle-induced X-ray emission Fig. Principle of particle-induced X-ray emission
Fig. Principle of particle-induced X-ray emission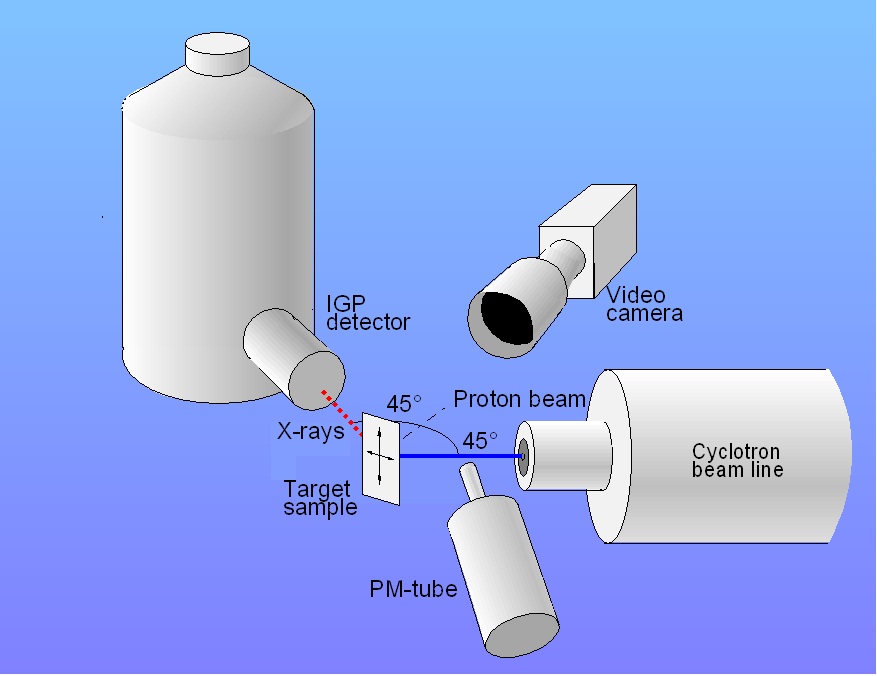 Fig. Schematic picture of PIXE set-up
Fig. Schematic picture of PIXE set-up
Particle-Induced X-ray Emission Analysis (PIXE)
Principle
A 3 MeV proton beam produced with the Åbo Akademi MGC-20 cyclotron
is used to
generate characteristic X-rays in a solid sample. The proton creates a
vacancy
in the inner electronic shell of the atom. The vacancy is filled with
an
electron from the outer shells. The energy can be released during the
de-excitation by the emission of an X-ray or an Auger electron. The
X-rays
originating from the electronic transition from the L- shell to the
K-shell are
usually referred to as Kα and
the transition from the M-shell is called Kβ
according to the Siegbahn notation.
The emitted
X-rays are detected with an energy dispersive Intrinsic Germanium
Planar (IGP)
detector with a 25 µm thick beryllium window. The concentrations
are obtained
by analyzing the X-ray
spectrum. The energy of the
emitted X-rays is characteristic for the elements in the sample. The
intensity
of the X- rays representing the element Z gives the elemental
concentration.
 Fig. Set-up for PIXE at Åbo Akademi University. The IGP detector is to left and the beam line to left. The vertical aluminum pipe is a collimator fot light into the PM-tube used for beam current monitoring.
Fig. Set-up for PIXE at Åbo Akademi University. The IGP detector is to left and the beam line to left. The vertical aluminum pipe is a collimator fot light into the PM-tube used for beam current monitoring.
Sample preparation
A special sample holder has been
constructed in
order to obtain a fixed measuring geometry. The
sample is then mounted on a computer controlled X-Y stage. The stage
used in this job is a commercial stepper driven X-Y stage (XYMR-8080,
Danaher
Precision Systems). The travel distances are 15 cm in both directions
and the
lead screw accuracy is 30 µm.With this scanning device
profiles of
elements are determined even at ppm level.
The irradiations are monitored using
an USB PC-camera (ToUcam, Philips).
 Fig. User interface for operating XY-stage to right and a view of sample to the left. The sample is a piece of wood.
Fig. User interface for operating XY-stage to right and a view of sample to the left. The sample is a piece of wood. For geological
samples 0.1 mm polished uncovered sections of minerals for
polarizing microscopy (frame 27 x 48 mm) are especially suitable.
Another
possibility is to mount the sample in a 5 x 5 cm slide projector frame.
Biological samples can be preconcentrated
by dry ashing at the Laboratory of
Analytical Chemistry in
order to enhance the sensitivity of the method. The ashes are pressed
to
pellets. Only a few mg of ash is needed for the analysis.
Calibration
In order to obtain quantitative results the peak areas in the X-ray
spectra
have to be normalized with respect to the integrated charge on the
sample (the
total amount of protons incident on the sample) during the irradiation.
The
integrated charge is determined utilizing light emission from N2
in
air excited by the proton beam. The light intensity, measured by a
photo-multiplier tube is proportional to the proton-beam intensity. The
method
has been developed at the Åbo Akademi
Accelerator Laboratory. The X-rays spectra are analyzed by using the GUPIX software.
The calibration
of GUPIX is evaluated by utilizing international standard reference
materials.
Special features